
B) While you may be a genuine buyer, our experience in the past has not been great with too many browsers and not many buyers. There are two reasons: A) The deliverables are our intellectual property, and we cannot share the same.
We are sorry, but we cannot send or show sample deliverables.
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELLING TUTORIAL HOW TO
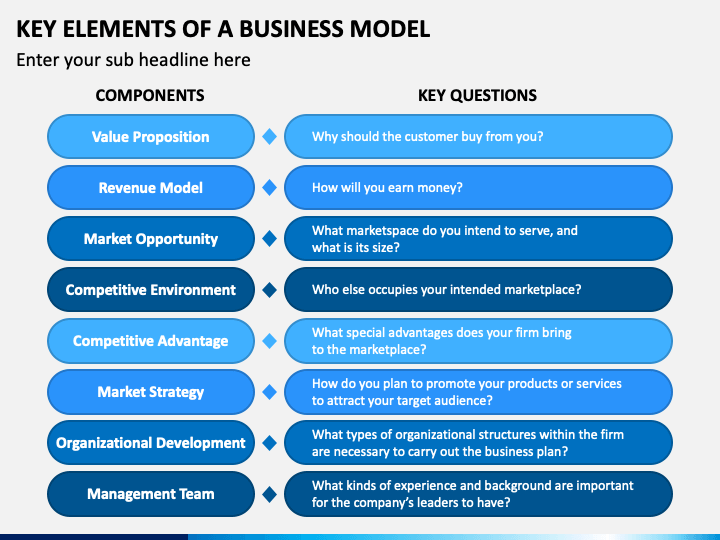
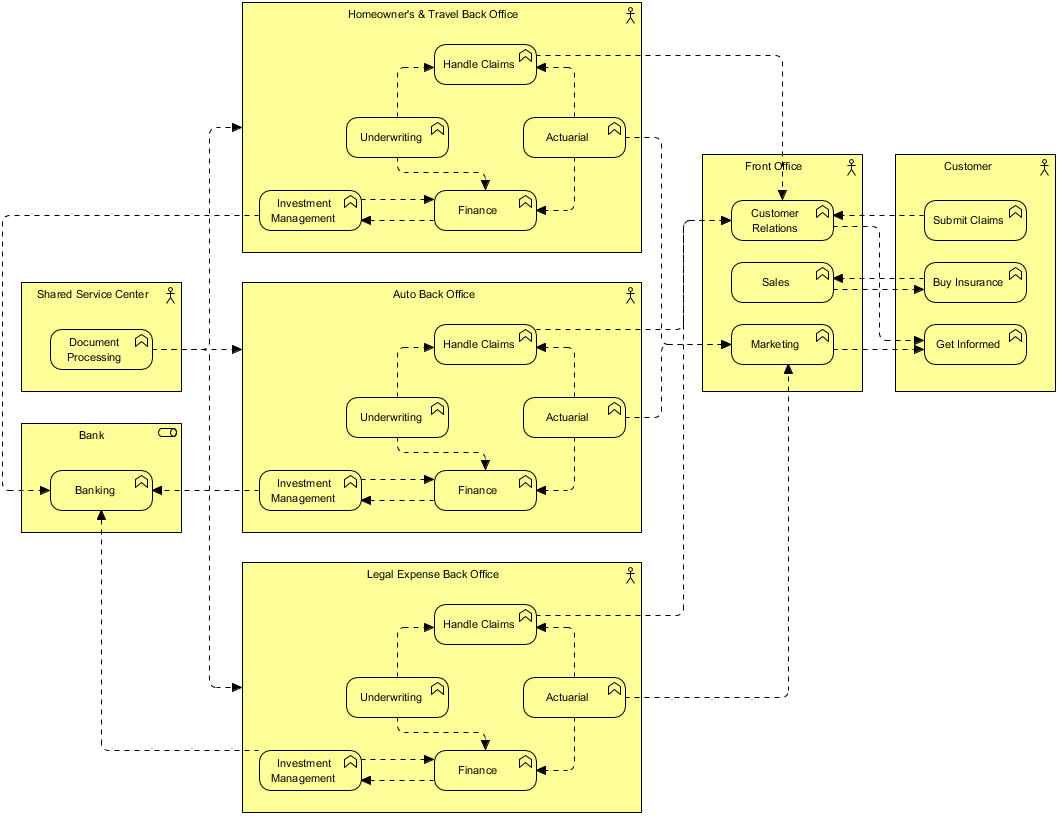
What are your thoughts on how to analyze a business process? And what is your opinion on how business processes are an integral part of business architecture via the Value Streams? (How to define a process model and how to reengineer a process are topics for a separate insight.) It may involve a variety of remedies based on what emerges from the business process analysis. Once you understand the fundamental process flow characteristics, determining an approach to how to improve a process comes next.

Bottlenecks – where available capacity is lower than the demand from the next process step.Hence it is important to identify the constraints through an in-depth business process analysis. Identifying the Constraints of a Process: Each process will have some inherent constraints, which in turn will make the process sub-optimal and cause it to underperform. Improving the capacity helps enterprises generate more with less and the following are some of the levers for increasing and optimizing the capacity of a business process. The capacity is the amount of input that can go into or the amount of output that can be created by a process, while holding resources and time steady. The understanding of the capacity of a business process is a key parameter in process analysis. Some of the key concepts for analyzing a business process: The Capacity of a Process: Inputs/Outputs – The inputs that are transformed in a process leading to the outputsĪnalysis of a Business Process: How do you analyze a business process.Task – The lowest level of granularity in a process flow, a task is self-contained action, performed by an actor or the system.An example could be a prospect filling in “Attend a webinar” form on a website as a part of the “Website conversion” sub-process. Activities – An act completed by a user or the system as a part of the process.An example could be “Website conversion” within the “Prospect to Customer” major process Sub-Process – A logical and complete process within a major process that lends itself to a hierarchical decomposition.An example could be “Prospect to Customer” process flow



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
